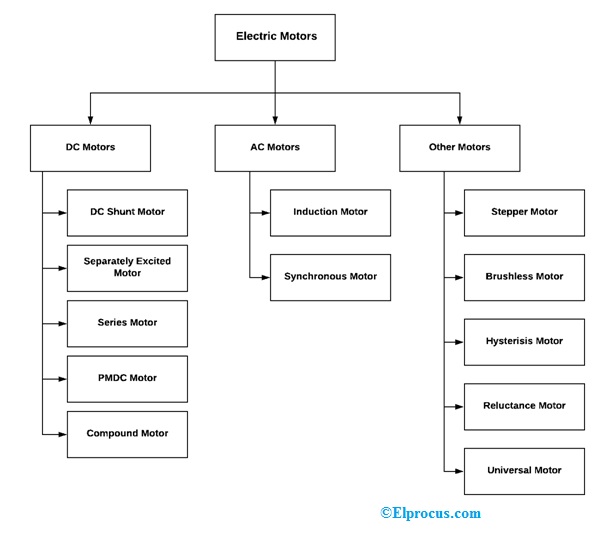
Electric car motors are the heart of electric vehicles (EVs), influencing their performance, efficiency, and overall design. Understanding the various types of electric car motors and their specific functionalities is essential for anyone interested in the automotive industry and the future of sustainable transportation. This article delves into the different types of electric motors, focusing on their effectiveness, and highlighting areas where improvements can be made. We’ll examine the advantages and disadvantages of each motor type, including factors like cost, maintenance, and power output. By understanding these nuances, EV enthusiasts, manufacturers, and researchers will gain valuable insights into the evolving world of electric vehicles.
AC Induction Motors: The Workhorse of EVs
Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
AC induction motors are a popular choice for electric vehicles due to their robust construction and relatively low cost. These motors operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a rotating magnetic field induces current in a stationary conductor, creating torque. Their simplicity contributes to their cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for mass production. Their efficiency, however, can vary depending on factors like load and speed. For instance, a study by the University of Michigan found that the energy consumption of AC induction motors can differ significantly depending on the vehicle’s acceleration profile. However, manufacturers are continuously working to optimize their efficiency, aiming to reduce energy loss through advanced control systems and materials. One example of this optimization is seen in Tesla’s early EVs, which incorporated improvements to AC induction motor efficiency to provide a more comprehensive driving experience.
Drawbacks and Applications
While AC induction motors provide reliable power, they generally have lower efficiency compared to permanent magnet motors, especially at lower speeds. This limitation might pose a challenge for applications requiring high acceleration or a wide range of speeds. In specific EV applications, such as smaller, lower-cost vehicles, they remain a pragmatic solution. For instance, many smaller electric cars leverage this motor type due to its accessibility and affordability.
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors: High-Performance Powerhouses
Enhanced Efficiency and Performance
Permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs) are known for their high efficiency and exceptional performance, particularly at higher speeds. Their design incorporates permanent magnets in the rotor, which create a strong magnetic field, resulting in superior torque production. This, in turn, leads to quicker acceleration and higher top speeds. This advantage makes them suitable for performance-oriented EVs, such as sports cars and high-end vehicles. Companies like Porsche and Audi are actively utilizing PMSMs in their EV models to achieve optimal driving experiences and performance.
Complexities and Considerations
Despite their superior performance, PMSMs come with a higher price tag due to the specialized materials and manufacturing processes required. Rare earth elements used in the creation of these permanent magnets have become a concern in the EV market. This complexity and the high cost might limit their use in mass-produced EVs. However, advancements in magnet technology and manufacturing are continually reducing costs and increasing availability, potentially broadening their application in the future.
Brushless DC Motors: A Flexible Choice
Versatile Applications
Brushless DC motors (BLDCs) offer a balance between efficiency and cost, making them suitable for various electric vehicle applications. Unlike AC induction motors, BLDCs do not rely on external power for magnetization and can often provide greater efficiency with proper control. The controllability of BLDC motors makes them suitable for various functionalities, such as power steering and vehicle ventilation. The flexibility of these motors allows for diverse applications in automotive, industrial, and consumer products.
Technological Advances
Advances in power electronics and control technology have significantly enhanced the efficiency and performance of BLDCs in recent years. These enhancements have led to more refined control systems, enabling precise torque and speed control in EVs. Further advancements focus on reducing the overall size and weight of the motors, thereby making them more integrated into the vehicle’s design.
Other Emerging Technologies: Exploring the Future
Solid-State Motors
One emerging technology gaining traction in the realm of electric car motors is the solid-state motor. The development of solid-state devices to replace traditional windings in electric motors promises to revolutionize motor designs. Theoretically, they could enhance efficiency and improve cooling. However, these technologies are still in the research and development phase, awaiting improvements and broader adoption.
Further Advancements
Ongoing research and development in various motor designs, including high-temperature superconducting motors, are potential game-changers for EV technology. These advancements could lead to enhanced efficiency and reduced motor size in future electric vehicles.
Motor Selection Factors
Performance Requirements
The selection of the optimal motor type for an electric vehicle depends largely on the performance requirements. For example, a high-performance electric vehicle will require a different motor type than a smaller, more budget-friendly model. Considerations regarding the required acceleration and top speed heavily influence motor selection decisions.
Cost Analysis
The associated costs for each motor type, including manufacturing, materials, and maintenance, also influence the final selection. The different costs and availabilities of the materials affect the price of the final product. The choice of motor type often involves a careful balance between performance and cost.
Understanding Efficiency Metrics
Measuring Motor Efficiency
Several metrics help to gauge the efficiency of electric car motors. These metrics often include the motor’s energy consumption, power output, and overall efficiency over various operating conditions. A detailed examination of these metrics aids in making informed comparisons and selections.
Case Studies
Real-world studies comparing the efficiency of different motor types in various EV models offer significant insights into their practicality and effectiveness. For instance, recent studies suggest that permanent magnet synchronous motors consistently demonstrate a notable advantage in terms of efficiency compared to AC induction motors, especially at higher operating speeds.
The Future of Electric Car Motors
Technological Trends
The future of electric car motors is bright, with continuous technological advancements aiming to enhance efficiency and performance. The utilization of advanced materials and control systems will lead to improvements in motor design. This design enhancement aims to minimize energy loss and maximize overall power output.
Innovations
Ongoing research and development in motor technology promise further innovations and enhancements. These innovations are expected to shape the future of electric vehicles, impacting sustainability and performance within the industry.
Sustainability Considerations
Material Sources
The sourcing of materials used in electric car motors is critical for sustainability. The environmental impact of the extraction, processing, and disposal of these materials is a growing concern. The sustainability and ethical sourcing of materials are crucial in the future of electric vehicles.
Waste Management
The effective management of motor waste during the vehicle’s lifespan is a significant factor. This aspect is particularly important given the increasing number of electric vehicles on the road.
Conclusion, Efficiency, and Cost
Conclusion, Efficiency, and Cost
The choices of electric car motors are ever-evolving, with ongoing improvements. There’s a significant emphasis on developing more efficient and cost-effective motors. The cost of electric car motors is a complex issue, and it will be interesting to see how these factors affect the future of electric vehicles. The importance of these factors in the overall sustainability and performance of electric vehicles is clear.
Cost, Performance, and Efficiency
These three elements must be carefully considered together to make a selection decision. Each motor type exhibits unique performance attributes, and the overall efficiency needs to be balanced with economic considerations.
In conclusion, exploring different types of electric car motors is crucial for understanding the advancements and future of sustainable transportation. From the efficiency of AC induction motors to the potential of permanent magnet motors, each type offers unique advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right motor depends on various factors, including cost, performance requirements, and overall design goals. Understanding these elements is vital for the electric vehicle industry to continue its progress. Further research into motor design, materials, and control systems will lead to even more efficient and powerful electric car motors, driving the adoption of EVs globally. If you’re interested in learning more about electric vehicle technology, explore resources like the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) or the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI).