
Choosing Your Charge: Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Charging Demystified
Electric vehicles (EVs) are rapidly gaining popularity, but one major concern for potential buyers is charging. Understanding the different charging levels—Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast charging—is crucial for a smooth transition to electric mobility. This guide demystifies each option, exploring their features, costs, and suitability for different use cases. We’ll help you understand which charging method is best for your daily commute, weekend road trips, and overall driving habits. Get ready to navigate the world of EV charging with confidence!
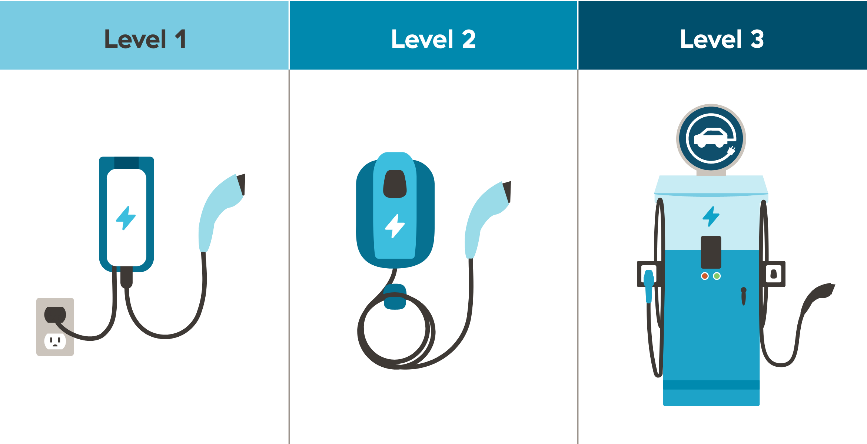
Level 1 Charging: The Basics
Understanding the Fundamentals
Level 1 charging utilizes standard household outlets, making it the simplest and least expensive charging method. This method is ideal for drivers who primarily use their vehicle for short commutes or who have the luxury of leaving their vehicle plugged in overnight. The charging speed of this method is extremely slow and can vary between outlets, but will usually take between 6-12 hours for a full charge, if your EV is able to take advantage of the home charging station.
Advantages and Disadvantages
One of the major advantages of Level 1 charging is its affordability. As it leverages existing household outlets, there are no extra costs associated with purchasing new infrastructure. However, the slow charging speed is a significant drawback. It’s particularly unsuitable for drivers with longer commutes, as the charge may not be sufficient for their daily driving needs. Charging overnight is an advantage and many drivers have no issues charging this way, so this option is ideal for them. The simplicity and ease of implementation make it a solid option for most.
Case Study: Frequent Short Trips
A user who commutes to and from work each day and doesn’t drive far, may find this option quite effective. Given that their commute is within range and doesn’t require a full charge, this option saves significant money as they only have to charge overnight and doesn’t require a dedicated charger on their property.
Data Point: Average Charging Time
On average, Level 1 charging takes anywhere from 6 to 12 hours, depending on the specific vehicle and the availability of electricity. This method is suitable for frequent overnight charging, but not ideal for those seeking faster charging options.
Connecting the Dots
Level 1 charging is best suited for users that don’t have many miles to drive or for those that prefer to charge the car overnight
Level 2 Charging: The Mid-Range Option
Delving Deeper into Level 2
Level 2 charging offers a significant improvement over Level 1 in terms of charging speed. It utilizes a dedicated charging station with a higher power output, enabling faster charging times. These Level 2 chargers are more expensive to install, but the increased speed and convenience make them a popular choice for regular EV drivers. Many companies install these Level 2 charging stations in their parking lots for employee convenience, and can also be set up on private property. This is significantly more expensive and requires professional installation for most scenarios.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The primary advantage of Level 2 charging is its speed. It can charge a vehicle’s battery from 0% to 80% in around 4-6 hours depending on the charger’s kW, which is much faster than the 10-12 hours required for Level 1. The initial investment in a Level 2 charger is often offset by the reduced charging time, saving both time and money for most drivers. However, Level 2 chargers require a dedicated installation process, which can be inconvenient and potentially expensive.
Case Study: Balancing Cost and Speed
A user with a longer daily commute can significantly benefit from the increased speed of Level 2 charging. The longer commute requires a higher capacity for the car to handle daily use and Level 2 offers just the speed needed without costing a significant amount of extra money.
Data Point: Common Charging Power
Many Level 2 chargers operate at 7.2 kW or 11 kW, but other models exist. These power outputs significantly enhance charging speeds compared to Level 1 charging, making them more efficient for daily use.
Bridging the Gap
Level 2 charging provides a strong middle ground between the slow speeds of Level 1 and the high costs of DC fast charging. This balance is essential for drivers who frequently use their EV for daily travel and require a practical and balanced method
DC Fast Charging: The Speed Demon
Understanding DC Fast Charging
DC fast charging offers the fastest charging speeds available for electric vehicles. These stations leverage direct current (DC) power, significantly increasing charging rates compared to Level 1 and Level 2. This method is ideal for long-distance travel or situations requiring rapid charging. It often charges in about 20-45 minutes, depending on the model. This makes it suitable for travelers looking to quickly add a large percentage to their EV’s range. This technology, however, often comes with a premium.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The primary advantage is the speed. Charging a vehicle from 20% to 80% can take as little as 20-45 minutes, making it a game changer for long-distance travel. However, DC fast charging stations typically have higher electricity rates and are generally found in designated locations or are often commercial.
Case Study: Long Distance Trips
For individuals traveling long distances, DC fast charging is the optimal solution, providing ample time to recharge and resume journeys. It allows drivers to avoid significant delays and continue their travel plans without any problems.
Data Point: Charging Time Range
Charging times vary widely, dependent on the vehicle’s battery capacity and the specific DC fast charger’s power output. But on average, DC fast charging enables 80% charge in approximately 20-45 minutes.
Connecting the Dots
DC Fast charging is the most expensive option but is excellent for fast charging on the go, offering significant time savings on longer trips.
Choosing the Right Charge for You
Considerations for Your Specific Needs
Your choice of charging method should align with your driving habits, location, and budget. For regular commuters, Level 2 charging often provides an excellent balance of speed and affordability. Long-distance travelers may find DC fast charging most convenient. Consider your daily commute and potential future travel plans in making this decision.
User Preferences and Driving Habits
Drivers with daily commutes and road trips should take into account the charging time and cost when deciding which method will work best for them. Those who don’t need to charge frequently can utilize simpler methods.
Budget Constraints
One significant factor to consider is budget. Level 1 charging is usually the least expensive, whereas DC fast charging stations are typically the most expensive. Evaluating your budget, current electricity costs, and expected charging frequency will help in this consideration.
Infrastructure Availability
The location of charging stations is another crucial factor to consider when choosing the right option for you. Availability of charging stations and the ability to install your own chargers will affect your daily driving.
Final Considerations
Each option has its unique strengths and weaknesses. Ultimately, the best solution is the one that meets your specific needs and priorities, balancing speed, cost, and accessibility.
Conclusion
Choosing Your Charge: Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Charging Demystified
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve outlined the nuances of each charging method. Choosing the ideal charging method will significantly depend on your needs and priorities. Whether you are an everyday commuter or a long-distance traveler, understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each method is critical for a smooth transition into EV ownership. Consider your specific needs and take into account the different charging methods when deciding which method will best suit your lifestyle and budget.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key differences between Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast charging?
Level 1 charging is the slowest and often the cheapest option, using standard household outlets. Level 2 charging is significantly faster, leveraging dedicated charging stations with a higher power output. DC fast charging provides the quickest charging times but is typically the most expensive option, particularly in commercial settings. Charging times, cost per kWh, and accessibility to stations vary greatly between each option.
How much does each type of EV charging cost?
The cost of charging depends heavily on electricity rates and the specific charging station. Level 1 charging is generally the least expensive, using your existing household electricity. Level 2 charging usually costs more than Level 1 due to higher power outputs, but it will still be more affordable than DC fast charging, especially over the long term. DC fast charging stations often charge significantly more per kWh due to the substantial power required. Ultimately, your electricity rates will be a major factor in determining your charging costs. You should always check the current rate at the charging station before plugging in your vehicle.
Which type of charging should I choose for my daily commute?
If your daily commute is relatively short and you don’t mind a longer charging time, Level 1 or Level 2 charging might be suitable. Level 2 charging, in particular, often offers a good balance of speed and cost. However, if your commute is longer and you need to refuel quickly, DC fast charging is more convenient, even if it comes with a higher cost per kWh.
In conclusion, choosing the right charging level for your electric vehicle hinges on factors like your driving habits, budget, and available infrastructure. Level 1 charging is suitable for occasional drivers with limited range needs and budget constraints, whereas Level 2 charging is perfect for regular drivers seeking a balance between speed and cost-effectiveness. DC fast charging excels for long-distance travel but comes with a premium price tag. This guide should empower you to make an informed decision, enabling a smoother transition to electric mobility! Ready to electrify your journey? Visit our website or call us today for more information!